Club fungi belong to the phylum Basidiomycota This phylum alongside the phylum Ascomycota constitutes the fungal subkingdom Dikarya The Dikarya subkingdom is considered toTHE CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI Fungi include puffballs, yeasts, mushrooms, toadstools, rusts, smuts, ringworm, and molds The antibiotic penicillin isThe kingdom fungi are made up of lichen, yeast, mushrooms, and moldsTable Contents the Fungi Kingdom010 Introduction Kingdom Fungi023 Fungi Facts052 How
Chapter 18 Concept 18 2
Club fungi characteristics
Club fungi characteristics-Fungi are heterotrophic organisms Fungi are filamentous, with the exception of unicellular yeasts The network of hyphae is known as mycelium Some hyphae are continuous tubes filled with multinucleated cytoplasm, these are called coenocytic hyphae and others have septae or cross walls in their hyphae The cell walls of fungi are composed ofA small clubshaped structure typically bearing four basidiospores at the ends of minute projections eukaryote A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles




Basidiomycota Fungi And Deuteromycota Fungi Youtube
Morels are Ascomycete Fungi 21 Basidiomycete or Club Fungi 22 Life Cycle of Basidiomycete Fungi 23 Bracket Fungi Puff Balls Mushrooms Jelly Fungi Basidiomycete Fungi that all produce Basiospores 24 Other Basidiomycetes Rusts and Smuts Rust infecting wheat leaves Rust infecting a Leaf Whitrot Smut digesting old wood 25 3 Other sac fungi have important uses a Penicillium is used as an antibiotic and to flavor some cheeses b Aspergillus flavors soy sauce and is also used in soft drink production 224 Basidiomycetes—The Club Fungi Club fungi include mushrooms, shelf fungi, coral fungi, puffballs, and stinkhorns 1The sterigmata are developed from a more or less clublike structure, called a basidium (pl basidia) for which the Basidiomycetes have been frequently named as club fungi The basidium was discovered by Levelle in 17 Mating Systems of Basidiomycetes About 10 per cent, of Basidiomycetes are homothallic
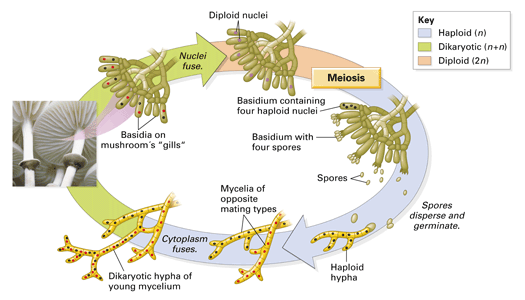
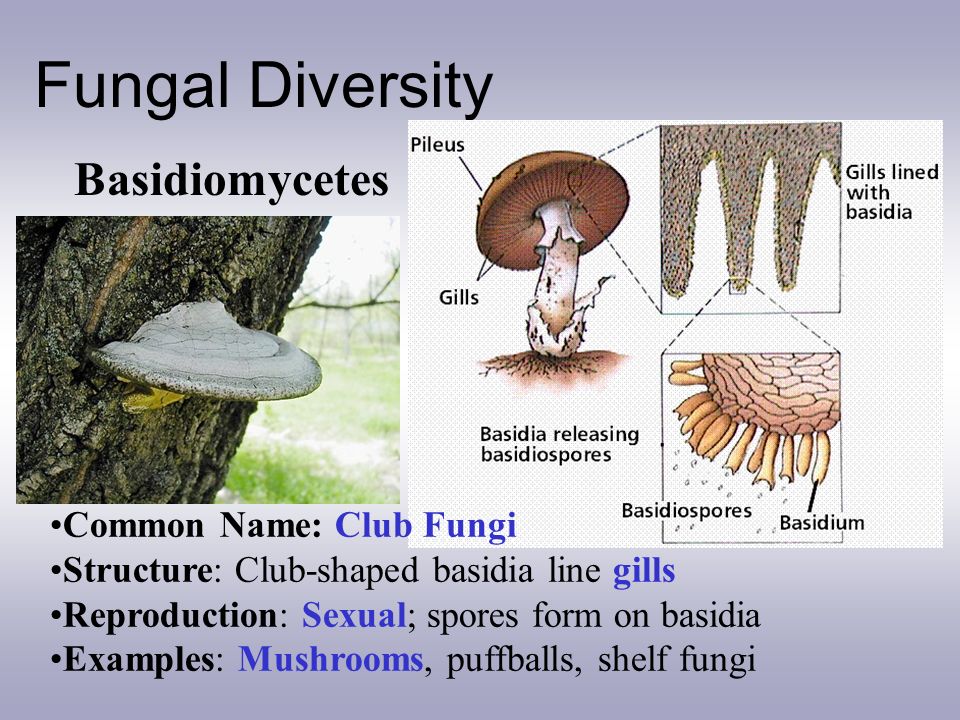
Basidiomycetes are often called club fungi because the cells (basidia) that bear the sexual spores resemble a small club Produced during its sexual cycle, it can bear millions of spores on clubshaped basidia located on the surface of its gillsADVERTISEMENTS It is formed by the germination of a basidiospore and contains a single haploid (n) nucleus in each cell It bears neither sex organs nor any basidia and basidiospores Read this BiologyWise article, which explains various characteristics of fungi The plural of fungus is "fungi", and it is one of the five kingdoms of organisms Kingdom Fungi is further grouped into four major subgroups;
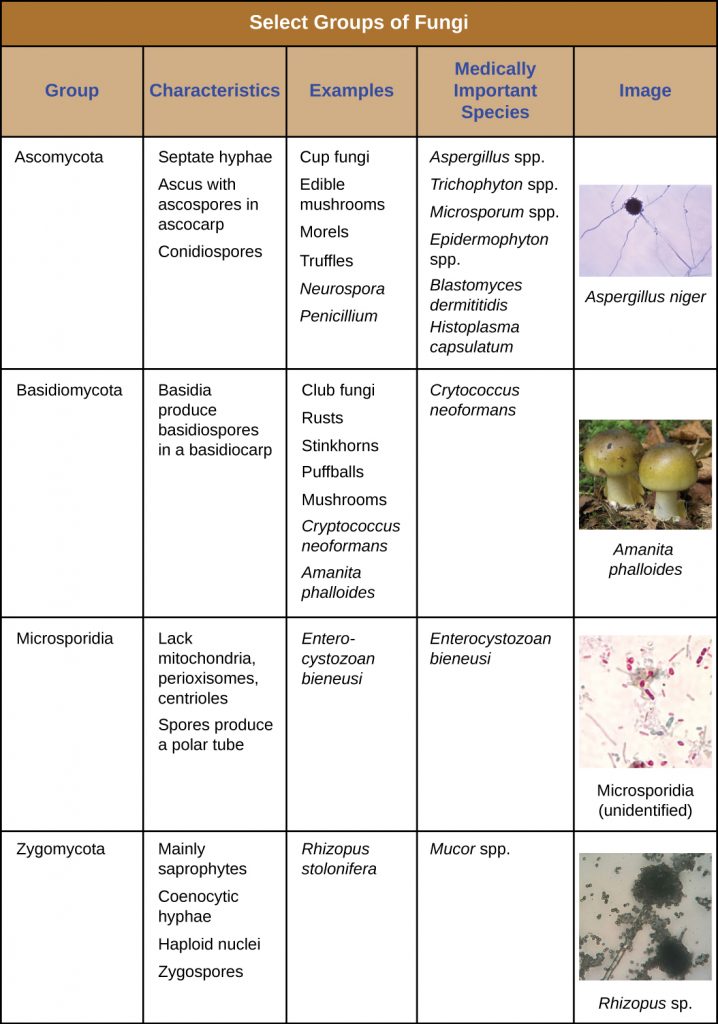
One of the characteristics that is common to all sac fungi is that reproduce through ascospores borne on sac like ascusThe ascospores are released by breaking the wall of ascus The ascospores of different members may be of varying size, shape and colourIn higher Ascomycotina the ascus are borne inside a protected fruiting body known as ascocarpCharacteristics of members of the Kingdom Fungi 4 are NOT plants because a Plants are autotrophs and fungi are heterotrophs Plants use photosynthesis to make their own food using chlorophyll and accessory pigments Fungi do not! This phylum contributes fungi used to make beer, bread, cheese, and medicines Examples include Aspergillus and Penicillium Phylum Basidiomycota The club fungi, or basidiomycetes, belonging to the phylum Basidiomycota produce basidiospores on clubshaped structures called basidia The phylum includes most common mushrooms, smut fungi, and rust




Characteristics And Major Groups For Fungi



Chapter 11 Protists And Fungi 7th Grade Science Kile Mingo
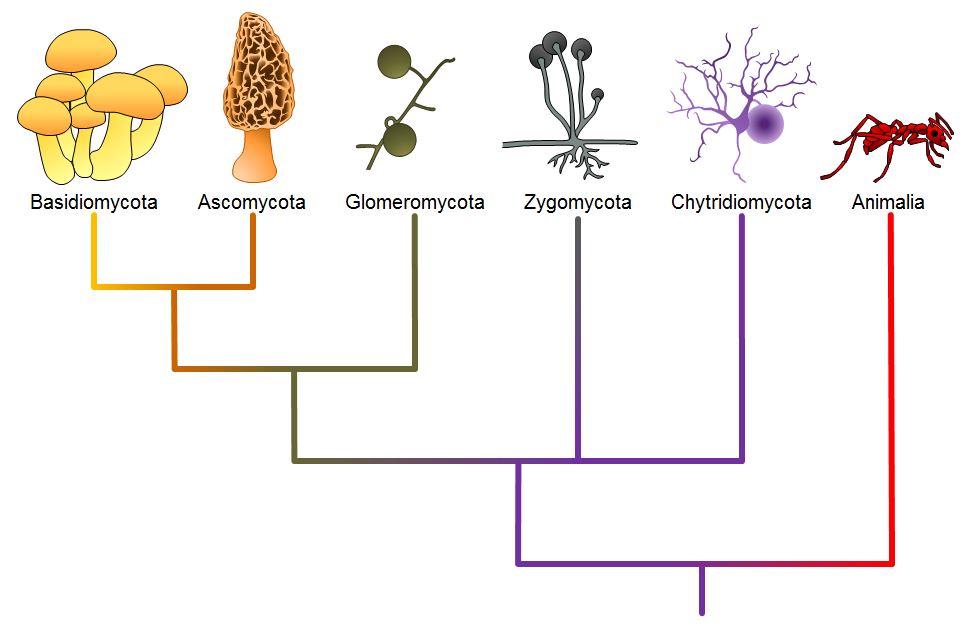
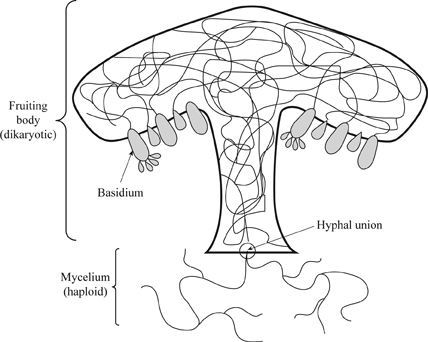
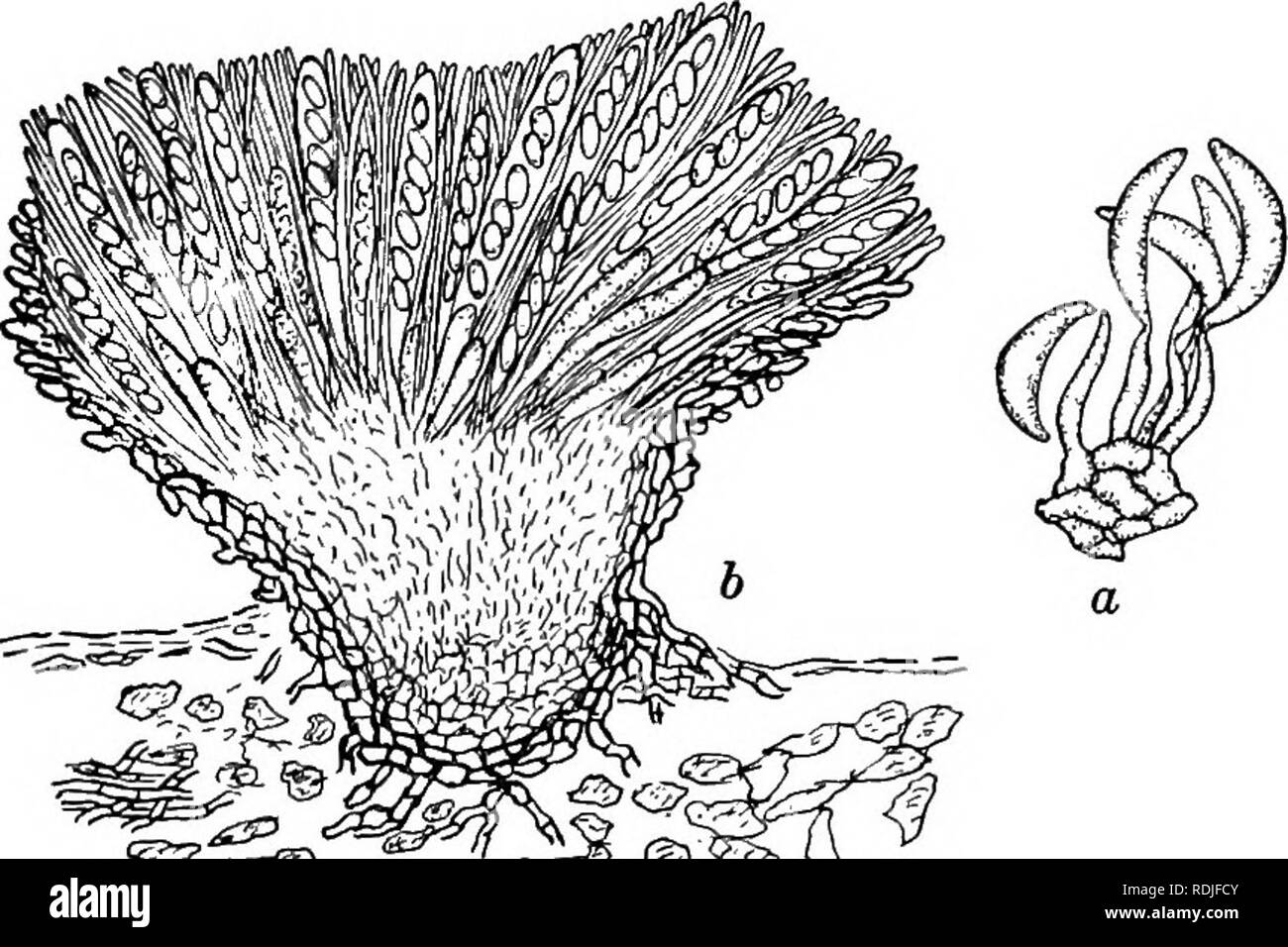
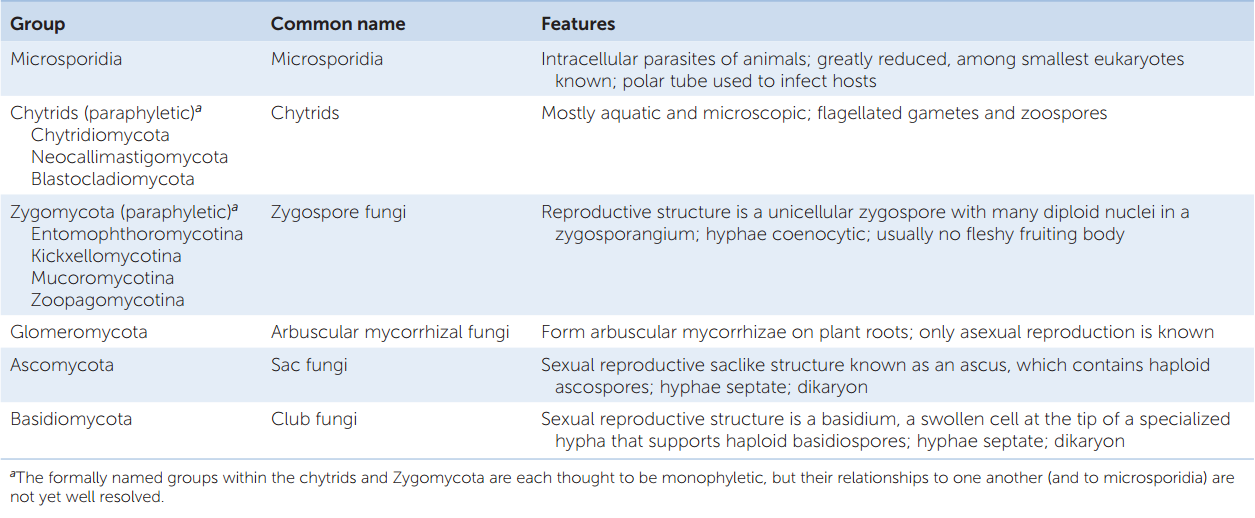
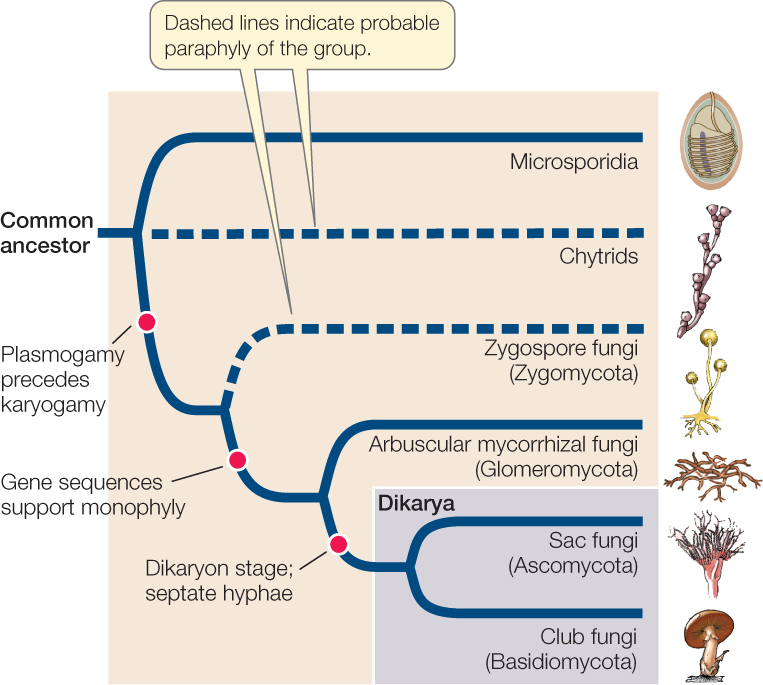
Rapid advances in molecular biology and the sequencing of 18S rRNA (ribosomal RNA) continue to show new and different relationships among the various categories of fungi The five true phyla of fungi are the Chytridiomycota (Chytrids), the Zygomycota (conjugated fungi), the Ascomycota (sac fungi), the Basidiomycota (club fungi) and the recentlyEdible mushrooms, noxious plant pathogens rusts and smuts, puffballs, and bracket/shelf fungi are all club fungi Basidiomycetes are called so for their characteristics, clubshaped (hence also called club fungi) sexual reproductive structure, the basidium (plural basidia)The division of fungi known as the club fungi, Basidiomycota, includes some of the most familiar fungi Mushrooms, puffballs, and shelf fungi are all members of this group, as are the plant rusts and smuts This group, which contains approximately 15,000 known species, is distinguished by the presence of a club shaped reproductive organ called the basidium




Powerpoint 5 Agarics Gilled Mushrooms Characteristics Flashcards Quizlet



Classifications Of Fungi Biology 2e
The Fungi Kingdom 2 Basidiomycota (Club fungi ) have a clubshaped part which produces the spores 3 Ascomycota (Sac Fungi) produce spores in saclike structures EX yeasts, cup fungi, powdery mildews, & lichens Lichens 4 Types of Fungi a fungus and an organism with chlorophyll (cyanobacteria or algae) that live togetherMushrooms, puffballs, and stinkhorns; They can be either singlecelled or multicellular organism Fungi consist of long threadlike structures known as hyphae These hyphae together form a meshlike structure called mycelium Fungi possess a cell wall which is made up of chitin and polysaccharides



Club Fungi King Of Kingdoms



Definition Of The Major Groups Of Fungi Chegg Com
Characteristics of Fungi Fungi are eukaryotic, nonvascular, nonmotile and heterotrophic organisms They may be unicellular or filamentous They reproduce by means of spores Fungi exhibit the phenomenon of alternation of generation Fungi lack chlorophyll and hence cannot perform photosynthesis What are the 5 characteristics of fungi?The algaelike conjugating fungi have a continuous mycelium containing hundreds or thousands of nuclei, with no divisions between them Species of conjugating fungi cause potato blight, downy mildew, black bread mold, and water mold (which affects dead leaves and sticks in water)



Basidiomycota




Basidiomycota Phylum Of Fungi Britannica
The five true phyla of fungi are the Chytridiomycota (Chytrids), the Zygomycota (conjugated fungi), the Ascomycota (sac fungi), the Basidiomycota (club fungi) and the recently described Phylum Glomeromycota The Deuteromycota is an informal group of unrelated fungi that all share a common character – they use strictly asexual reproductionBasidiomycota, large and diverse phylum of fungi (kingdom Fungi) that includes jelly and shelf fungi;The "male" strain produces an antheridium and the "female" strain develops an ascogonium At fertilization, the antheridium and the ascogonium combine in plasmogamy without nuclear fusion Special ascogenous hyphae arise, in which pairs of nuclei migrate one from the "male" strain and one from the "female" strain




Basidiomycota Fungi And Deuteromycota Fungi Youtube




Ppt Club Fungi Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
7) Describe the characteristics of the following fungal groups, include common names, replication, and example of fungi 1 Zygomycota aka conjugation fungi Black Bread Mold Zygomycota can produce spores either sexually, through conjugation, or asexually 2 Ascomycota aka sac fungi yeast, Penicillium notatum, P roquefortii, P camemberti, candida albicansGeneral Characteristics Phylum Basidiomycota includes mushrooms, toadstools, puffballs, jelly fungi, rusts, smuts, and shelf fungi Called "club fungi" after the shape of the Basidium the reproductive structure looks like the club suit in playing cards Many hallucinogenic, deadly, others safe and edible Complex life cyclesClub fungi can reproduce asexually, but sexual reproduction is more common They reproduce using spores Development Sac fungi grow hyphae from the spore The mycelia have a huge surface area Examples Some examples of club fungi include mushrooms, polypores, puffballs, boletes, and bird's nest fungi



Fungous Diseases Of Plants With Chapters On Physiology Culture Methods And Technique Fungi In Agriculture Ascomycetes 7 Shown In Fig 80 B The Asci Are Club Shaped And Bear Eight
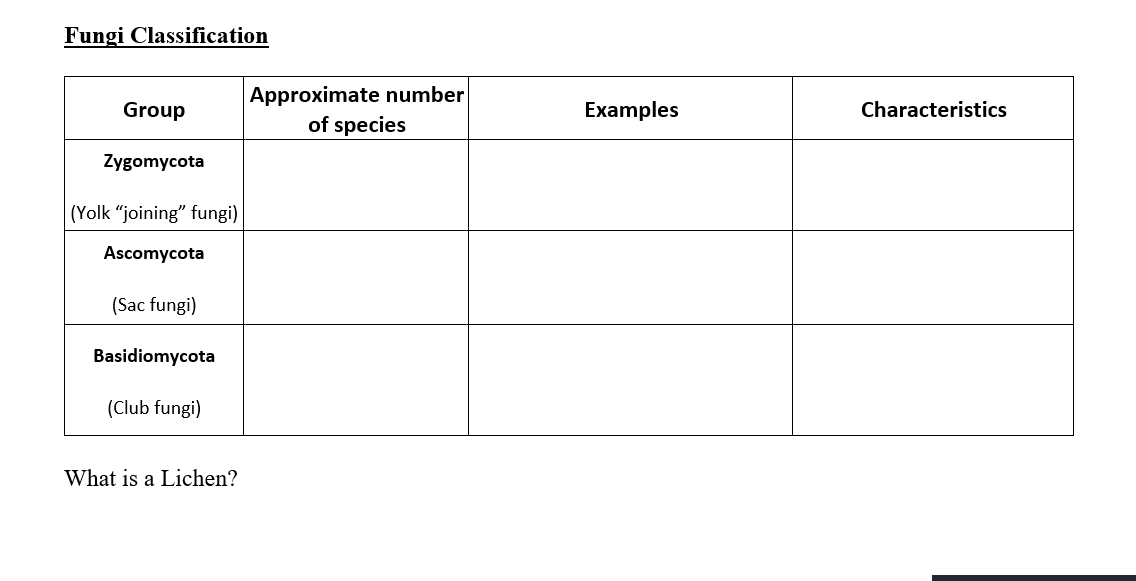



Solved Fungi Classification Group Approximate Number Of Chegg Com
Fungi reproduce by releasing spores from a fruiting body The fruit, called a mushroom, releases spores into the air, and the wind carries the spores off to start the next generation Around 100,000 species of fungi are divided into five phyla, based largely on the characteristics of their reproductive organs Club Fungi (Basidiomycota)And the rusts and smutsBasidiomycota are typically filamentous fungi composed of hyphaeMost species reproduce sexually with a clubshaped sporebearing organ that usually produces four sexual spores (basidiospores)The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium ), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hypha The basidia, which are the reproductive organs of these fungi, are often contained within the familiar mushroom, commonly seen in fields after rain, on the supermarket shelves,



Club Fungi King Of Kingdoms




The Fungi Chapter 23 Mader Biology 8th Ed Ppt Video Online Download
The "male" strain produces an antheridium and the "female" strain develops an ascogonium At fertilization, the antheridium and the ascogonium combine in plasmogamy without nuclear fusion Special ascogenous hyphae arise, in which pairs of nuclei migrate one from the "male" strain and one from the "female" strainThe clavarias, or club fungi (eg, Clavaria, Ramaria), are shrublike, clublike, or corallike in growth habit One club fungus, the cauliflower fungus ( Sparassis crispa ), has flattened clustered branches that lie close together, giving the appearance of the vegetable cauliflowerThe club and coral fungi provide a catchall for a variety of often only distantly related fungi Clavaria laeticolor, shown at farleft is as simple as such fungi can be but illustrates their essential characteristics The basidioma or fruiting body is a simple



Fungi




Chapter Fungi Section 1 Introduction To Fungi
The Basidiomycetes are known as club fungi due to the presence of club shaped ascuslike structure called as basidium Basidium is enlarged hyphae from which four haploid basidiospores are developed externally They are unicellular, uninucleate and haploid which germinate to form the new mycelium The life cycle of the club fungi consists of three phases, basidiospores, primaryFungi Characteristics Eukaryotes Cell walls made of chitin Mostly multicellular Heterotrophs (mostly decomposers) Hyphae Threadlike chains of cells that absorb nutrients Mycelium Club Fungi Examples Mushrooms, bracket fungi, and puffballs Club Fungi Reproduce using basidiaThey are imperfect fungi , sac fungi , club fungi , and conjugating fungi



Club And Coral Fungi




Fungi Lichens Office For Environmental Programs Outreach Services
These are among the most familiar fungi;Ans i) They are multicellular and eukaryotic organisms, ii) They do not have chlorophyll of their own, iii) Cell wall is made up of chitin, iv) Their body is formed of threadlike filamentous structures called hyphae, and v) Their mode of nutrition is saprophytic or parasitic It is a morphologically complex tissue and forms structures such as the typically mushroomshaped basidiocarps commonly seen in nature Sexual reproduction of the club fungi begins upon fusion of two primary hyphae to form a clubshaped structure, known as a basidium




Biological Diversity 4



Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota The Club Fungi The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium ), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hypha2 Club fungi have a clubshaped part which produces the spores 3 Sac Fungi produce spores in saclike structures EX yeasts, cup fungi, powdery mildews, & lichens Lichens 4 Types of Fungi a fungus and an organism with chlorophyll that live together •Example MushroomsCharacteristics Basidiomycota are unicellular or multicellular, sexual or asexual, and terrestrial or aquatic Indeed, Basidiomycota are so variable that it is impossible to identify any morphological characteristics that are both unique to the group and constant in the group




Hillis2e Ch22




Lesson Explainer Kingdom Fungi Nagwa
Types of Fungi Scientists often divide fungi into four groups club fungi, molds, sac fungi, and imperfect fungi Some of the more common fungi that you are likely to see or use everyday are described below Mushrooms Mushrooms are part of the club fungi group Mushrooms are the fruiting body of a fungusClub fungi (mushrooms), shelf/bracket fungi, smuts and rusts fruiting body of basidiomycetes Reproductive structures that produce sexual spores Spores produced in the basidia of




Basidiomycetes Club Fungi Coprinus Puccinia Graminis Microscope Slides Carolina Com




Clavulinopsis Laeticolor Handsome Clubfungus
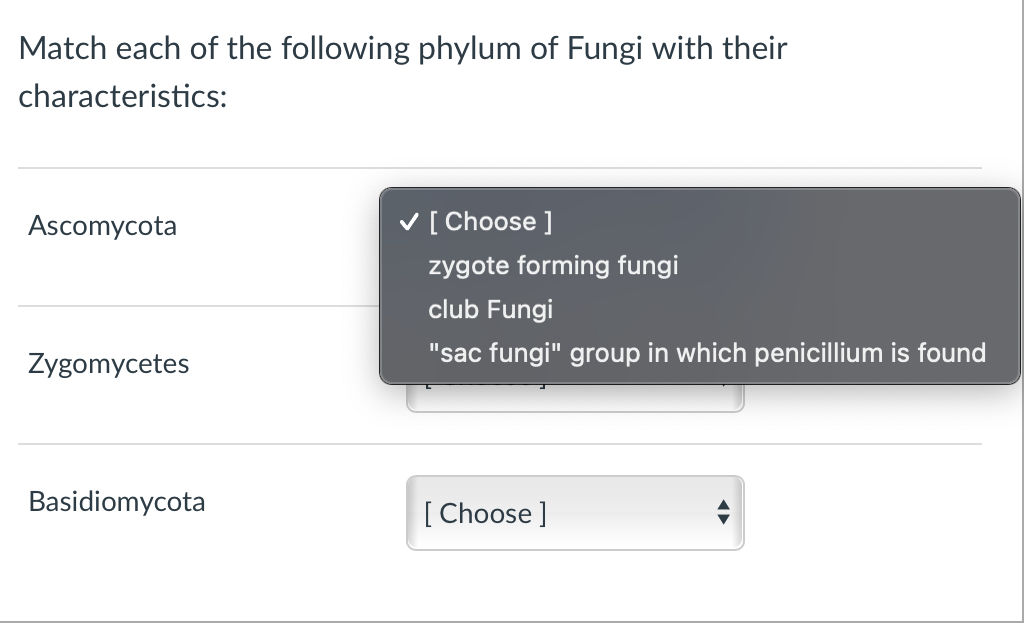



Match Each Of The Following Phylum Of Fungi With Chegg Com




Fungus Chapter Ppt Video Online Download



Hillis2e Ch22




Chapter Characteristics Of Fungi Belong To The Kingdom Fungi 1 Introduction To Fungi Fungi Unicellular Or Multicellular Chapter Eukaryotic Ppt Download



Basidiomycota




Fungi




Solved Your Team Members But Your Paper Must Be The Product Chegg Com



Characteristics Of Fungi Ppt Video Online Download




Classification Of Fungi Gymnomycota Mastigomycota Amastigomycota




Kingdom Fungi Study Of Fungi Mycology Common Characteristics



Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Sparknotes




Fungi Lichens I Characteristics Of Fungi A What




Classification Of Fungi Mycology Microbe Notes




Fungi Lichens I Characteristics Of Fungi A What




Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Biology For Majors Ii



Basidiomycota



Hillis2e Ch22



5 2 Fungi Microbiology Canadian Edition



Fungi



Club And Coral Fungi




Chapter 18 Concept 18 2




Mushroom Morphology Types Of Identifying Characteristics




Kingdom Fungi Ppt Download




Kingdom Fungi Characteristics Eukaryotes Ppt Download



Solved Match The Following Characteristics With The Correct Chegg Com




Club Fungi By Hunter Fritz




Ppt Chapter 22 Fungi Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
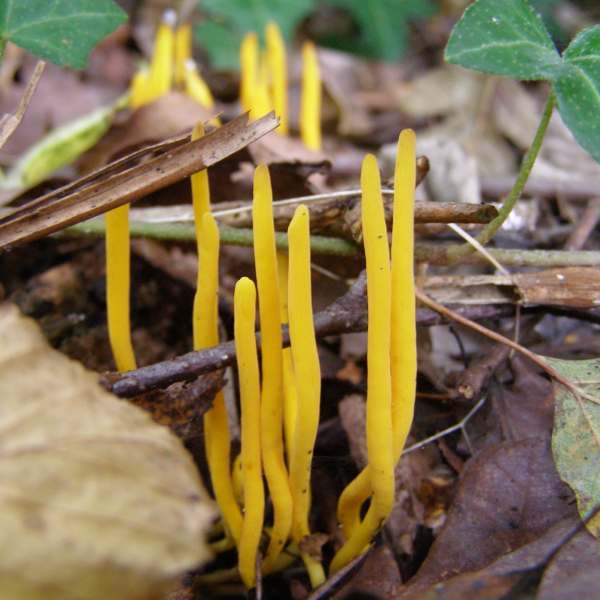




Clavulinopsis Laeticolor Handsome Clubfungus



What Is The Difference Between Ascomycota And Basidiomycota Pediaa Com




Amy B S Bio Blog Fungi



Fungi Presentation Biology



Page 469 Reviewing Your Knowledge Complete Table Chegg Com




Fungi Ppt Download



Classification And Importance Of Fungi




What Are The Characteristics Of Club Fungi Cement Answers




Solved Four Phyla Of Fungi Characteristics Phylum Examples Chegg Com




Chapter 23 The Fungi 2 Outline Characteristics Structure




Hillis2e Ch22




4 Gb 21 Cla Fun J Spr03




Chapter Fungi Section 1 Introduction To Fungi Ppt Video Online Download




Kingdom Fungi Basidiomycetes General Characteristics Of Club Fungi Youtube




Kingdom Fungi Characteristics Youtube



Fungi



Fungi




Ppt The Fungi Kingdom Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Chapter 23 The Fungi 2 Outline Characteristics Structure



Club And Coral Fungi




Characteristics Mycology All You Need To Know




Classification Of Fungi Phycomycetes Ascomycetes Basidiomycetes And Deuteromycetes




Chapter 21 Kingdom Fungi Notes Ppt Download




Biology 2e Biological Diversity Fungi Classifications Of Fungi Opened Cuny




Kingdom Fungi Characteristics Structure Schoolworkhelper
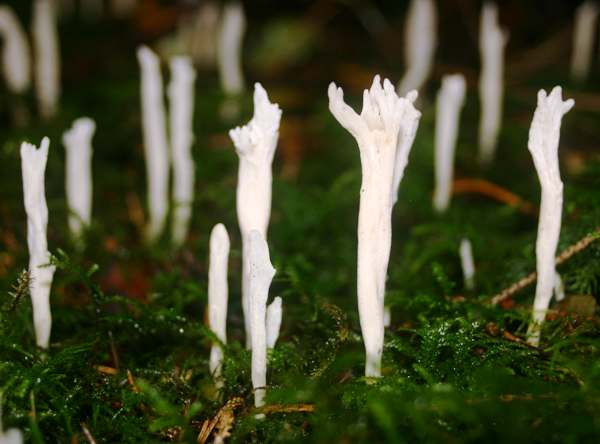




Clavulina Rugosa Wrinkled Club Fungus



Ascomycota
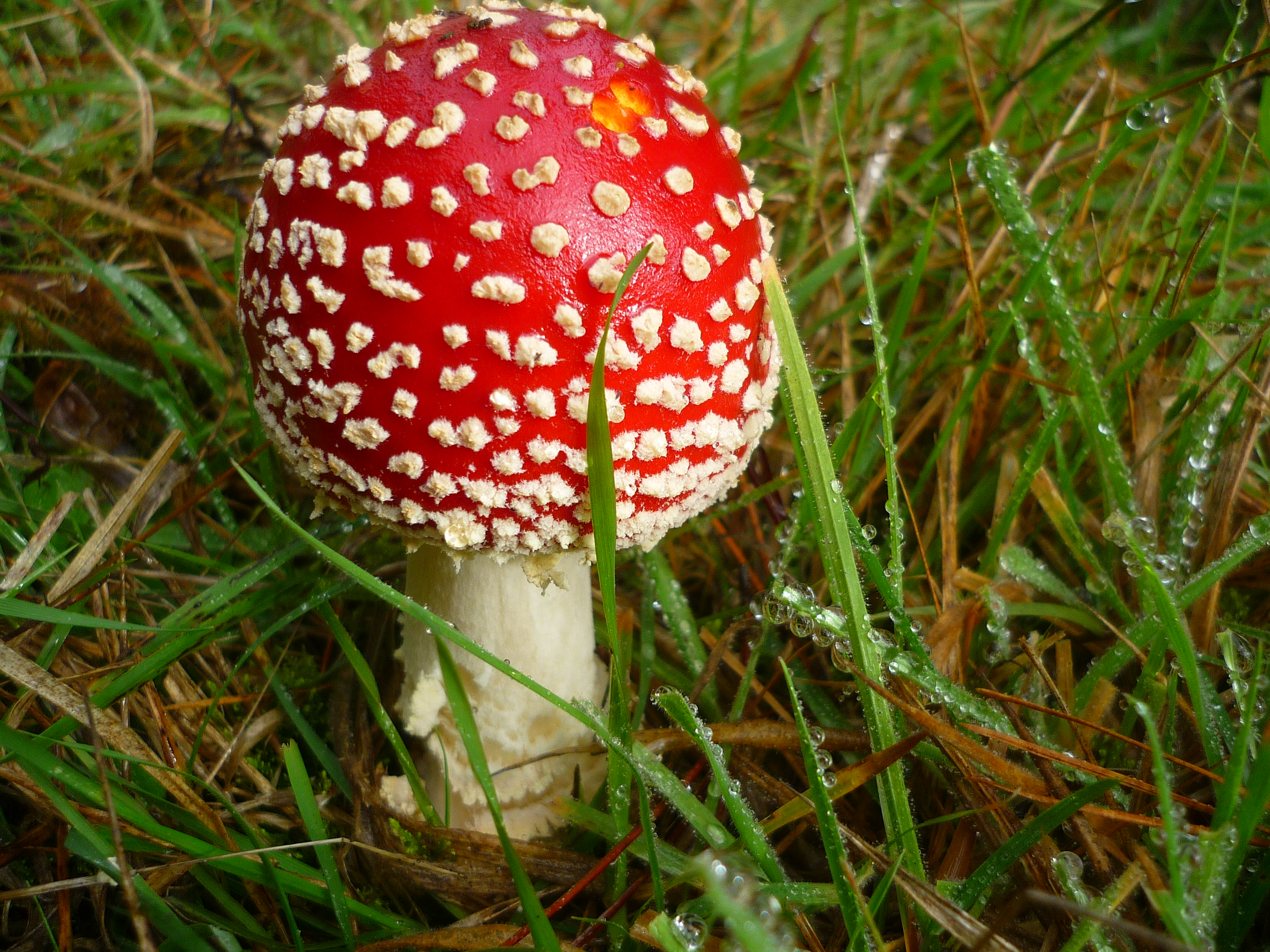




It S Fungus Time Freya S Research




Basidiomycota Life Cycle Of Ustilago Tritici Characteristics Of Club Fungi Chapter 8 First Year Youtube



Hamilton Local K12 Oh Us




Club Fungi Reproductive Structures Are Shown In The Image Below What Benefits Are There In Having Brainly Com




Exam Preparation Biology Study Material And Notes



Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Sparknotes
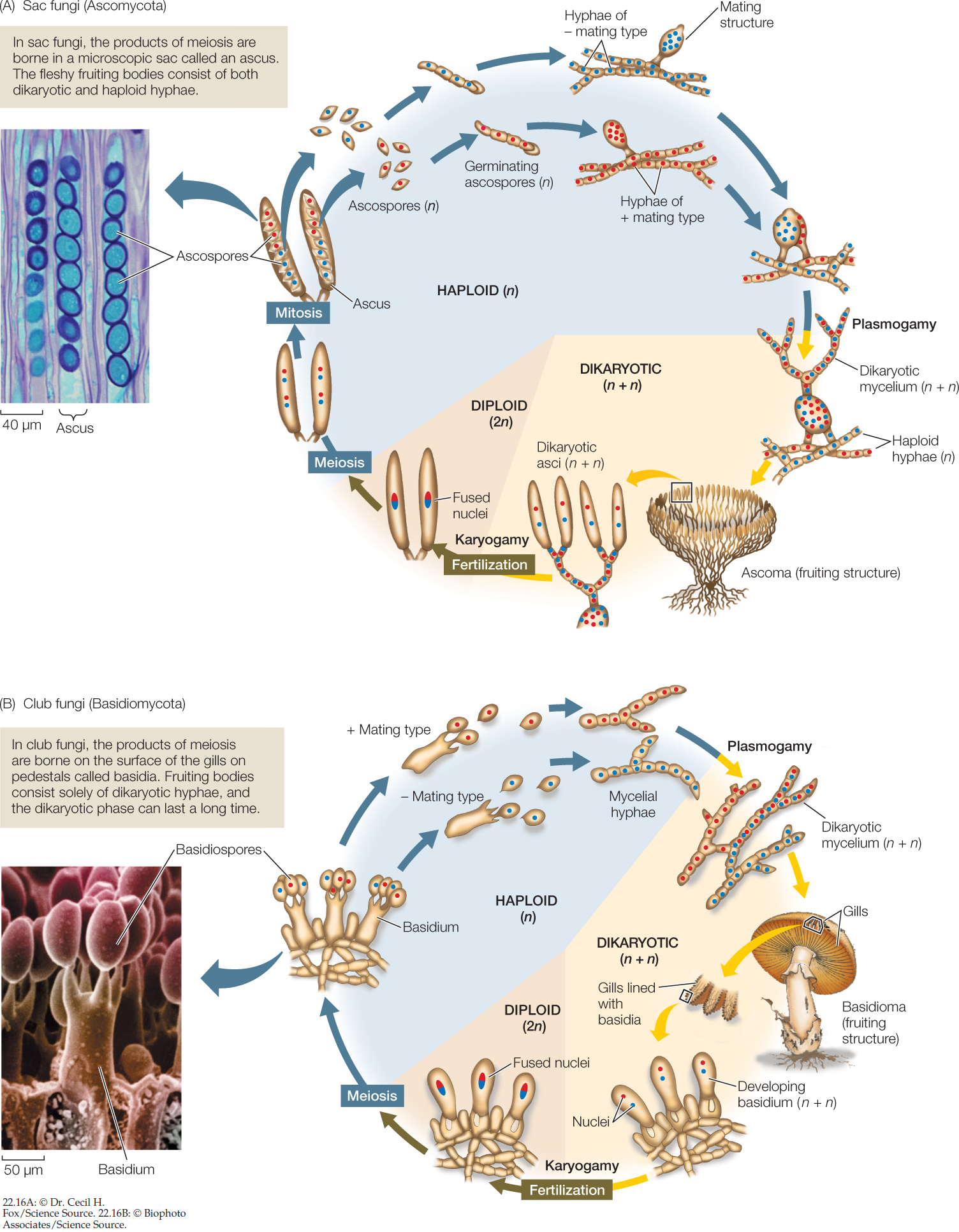



Hillis2e Ch22
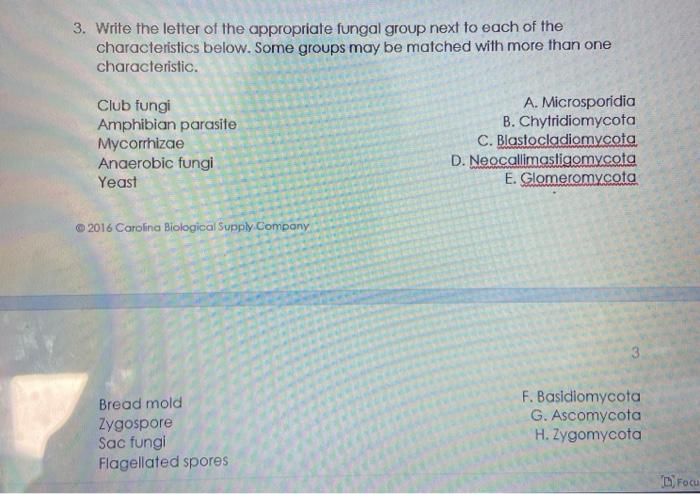



3 Write The Letter Of The Appropriate Fungal Group Chegg Com



Chapter 21 Kingdom Fungi Ppt Video Online Download




Kingdom Fungi Ppt Download
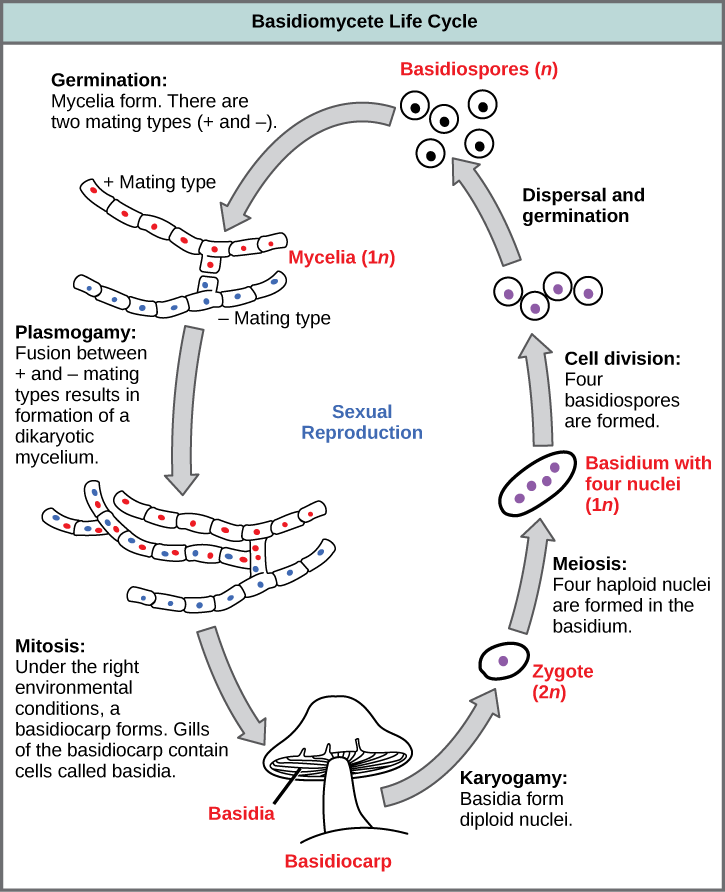



Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Biology For Majors Ii




Chapter 18 Concept 18 2




Ppt Kingdom Fungi Division Chytridiomycota Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
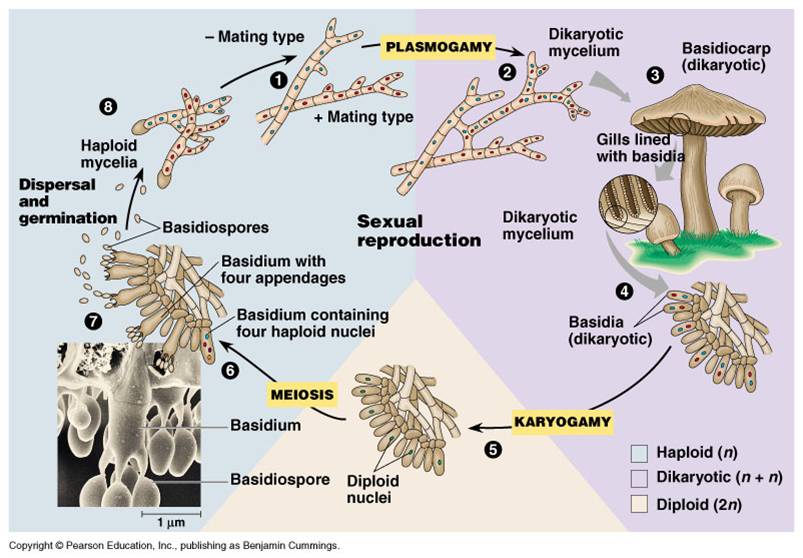



Classification Of Fungi Part 1 F Sc Biology Chapter 8
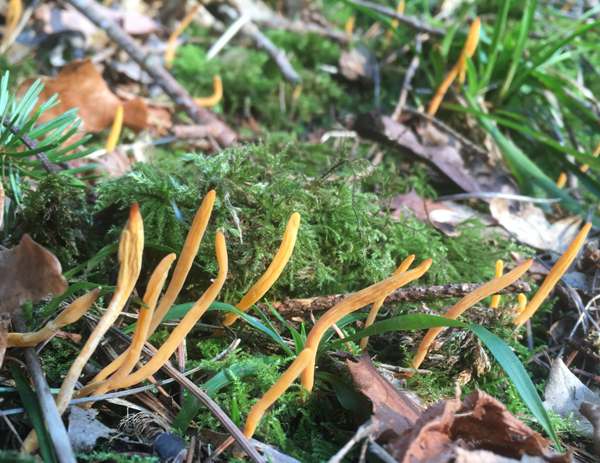




Clavulinopsis Laeticolor Handsome Clubfungus




Fungus Wikipedia



1



1




Fungi Lichens I Characteristics Of Fungi A What




Ppt Club Fungi Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Fa Griffin Weebly Com



Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Sparknotes




Kingdom Fungi Outcome Describe And Observe The Kingdom Fungi Ppt Video Online Download




Ch 22 Fungi Ppt Video Online Download



Club Fungi




Kingdom Fungi 1 Characteristics 2 The Characteristics Of



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿